11.2. Coriolis Force#
The fact that Earth rotates once every day on its axis results in a force acting on the wind. This force is called the Coriolis Force (CF), which is named after the scientist who quantified the relationship. In order for the CF to impact atmospheric motions, the flow must be going over large time and/or spatial scales. For example, the CF will NOT affect water draining out of your sink or bathtub because it will drain too quickly and is not draining over a large enough spatial scale. We can quantify the Coriolis parameter, \(f\), as follows,
where \(\phi\) is the latitude and Ω is the Coriolis constant, which is \(7.292 \cdot 10^{-5} s^{-1}\). The strength of the Coriolis parameter increases with increasing latitude (Fig. 11.2) and is maximized at the poles (not shown).
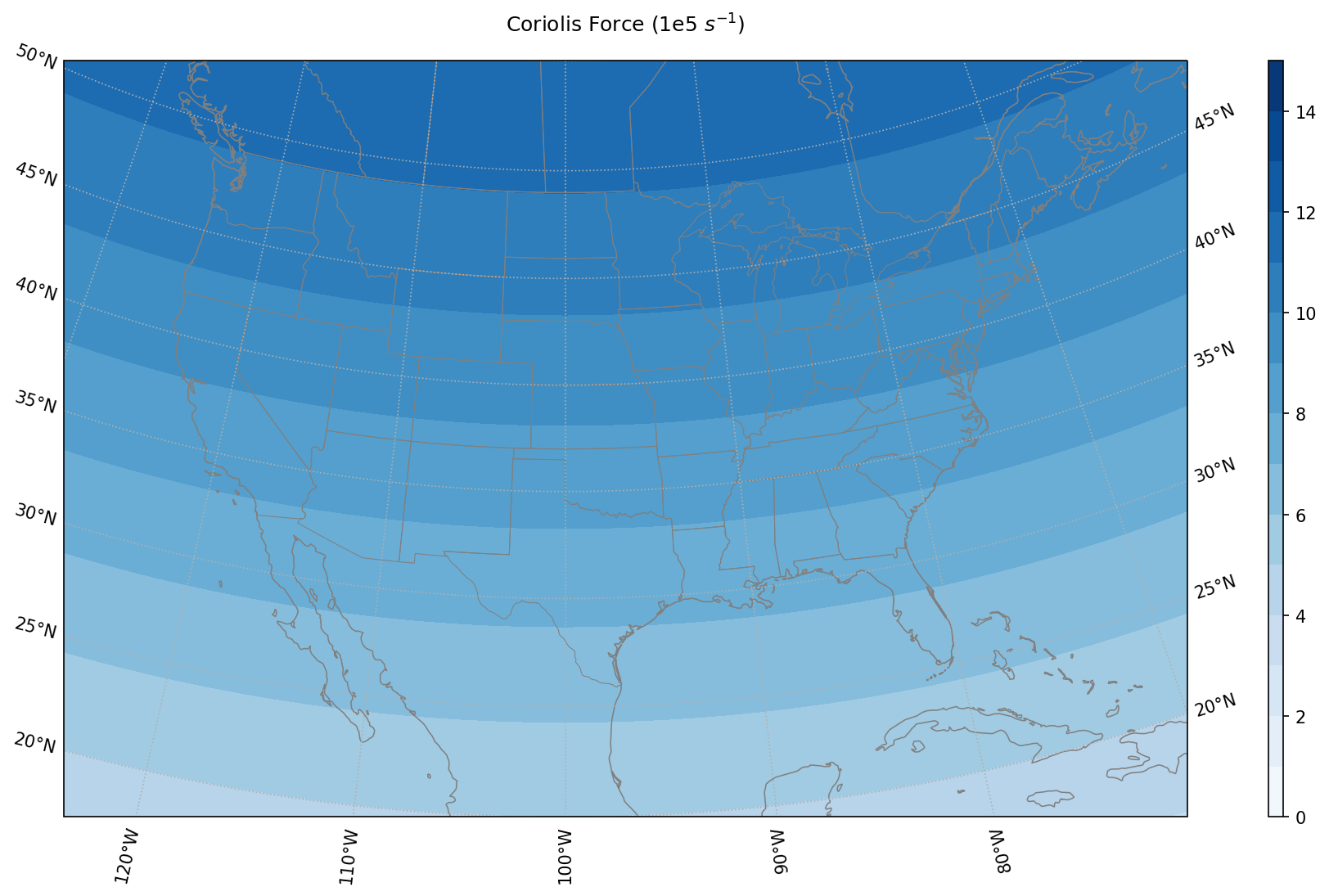
Fig. 11.2 This map shows the value of the Coriolis parameter, which is directly proportional to the latitude.#
The Coriolis force acts perpendicular to the wind at all times, it pulls the wind to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. The CF in the Northern Hemisphere can be written in a bulk sense as,
where \(V\) is the wind speed. The CF will only act on the wind, it cannot create the wind. If there is no wind, the Coriolis force is zero, because the wind is zero! Similarly, if you are at the equator, the Coriolis Force will also be zero because the Coriolis Parameter is zero! It shouldn’t be a surprise that the CF has the same units as the PGF, \(m\) \(s^{-2}\).
